2: Misinformation in Social Media
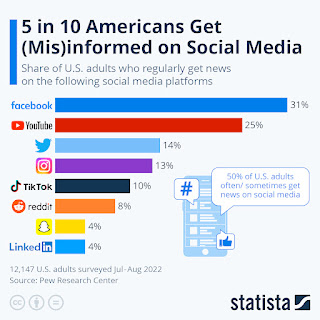
In today’s digital world, social media has changed how we communicate and share information. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram help us connect quickly, but they also allow misinformation to spread rapidly.
Misinformation is false or misleading information shared without the intent to deceive. It includes rumors, conspiracy theories, altered images, and misleading statistics. Unlike disinformation, which is shared to intentionally mislead, misinformation can be spread by people who believe it is true. Social media’s algorithms, which prioritize engagement over accuracy, help misinformation spread quickly.
Social media platforms use algorithms to boost content that gets a lot of attention. This often means that shocking or emotionally charged posts get more visibility, making misinformation more likely to go viral. Research has shown that false information spreads faster than true information. For example, a 2018 study in Science found that false news stories are retweeted 70% more often than true stories. This allows misinformation to reach millions of people before it can be corrected.
Another factor in the spread of misinformation is “echo chambers.” These are groups where people mostly hear views that match their own, which makes misinformation seem more believable. The speed at which information can be shared on social media means a single post can quickly reach a large audience, often outpacing traditional media corrections.
Misinformation can damage individual reputations. False claims can go viral, affecting people’s personal and professional lives. Many cases of online harassment and bullying stem from misinformation, highlighting its harmful effects on individuals. Fighting misinformation on social media is a complex challenge that requires cooperation from many parties, including tech companies, governments, and users.
Teaching people how to identify credible information is vital. Schools and educational programs can help users learn how to evaluate sources, recognize biases, and fact-check claims. A more informed public will be less likely to fall for misinformation. Social media companies have a significant role in reducing misinformation. They can create stricter policies for content moderation, improve fact-checking processes, and promote reliable sources. Making algorithms transparent can also help users understand how information is shared. Labeling misleading content and reducing its visibility can guide users away from false information.
Partnering with independent fact-checking organizations can improve the accuracy of information on social media. These organizations can verify claims and provide context, helping users navigate the vast amount of online information. Promoting fact-checked content can direct users towards reliable information. Users play a crucial role in how information spreads. Social media platforms can include reminders that encourage users to verify information before sharing it. By fostering a culture of responsible sharing, users can help prevent the spread of misinformation.
Misinformation in social media is a significant challenge that affects public health, democracy, and individual lives. The rapid spread of false information highlights the need for effective strategies to combat this issue. By promoting media literacy, holding platforms accountable, collaborating with fact-checkers, and encouraging responsible sharing, we can work towards a more informed society. As we navigate the digital landscape, everyone needs to contribute to a healthier information environment.






Comments
Post a Comment